
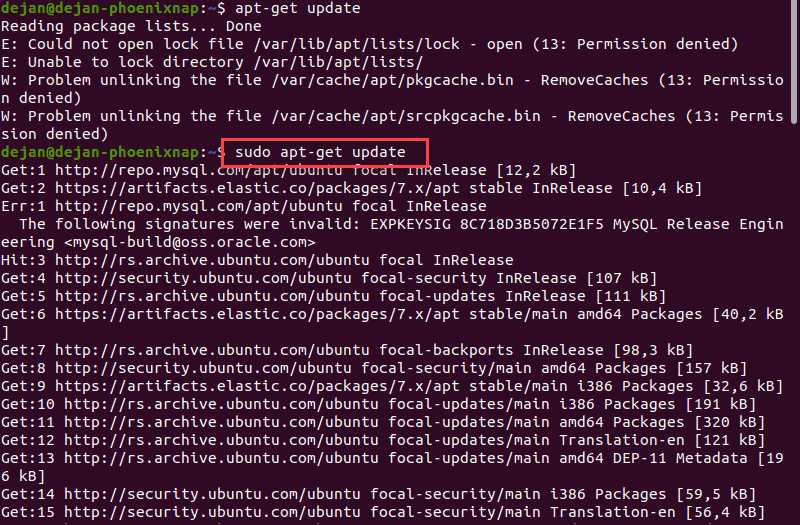
- CREATE A USER WITH SUDO PRIVILEGES LINUX FULL
- CREATE A USER WITH SUDO PRIVILEGES LINUX PASSWORD
- CREATE A USER WITH SUDO PRIVILEGES LINUX FREE
Add the following to your shell's configuration file: One way to make the next word expand is to make an alias for sudo ending with a space. This means that your aliases will not normally get expanded when running the sudo command. For example, add the following to your shell configuration file:Įxport SUDO_PROMPT=$'\a please enter a password: 'Īliases in Zsh and Bash are normally only expanded for the first word in a command. Is there an alternative, for example by using "-B" option as default? (Discuss in Talk:Sudo)Īnother option is to set the SUDO_PROMPT environment variable.

Reason: Is it possible to preserve the localized prompt while using bell? The same question for the case when SUDO_PROMPT is used. for pasting, one can usually use Ctrl+q instead. in vim, insert using the sequence Ctrl+v Ctrl+g.
CREATE A USER WITH SUDO PRIVILEGES LINUX PASSWORD
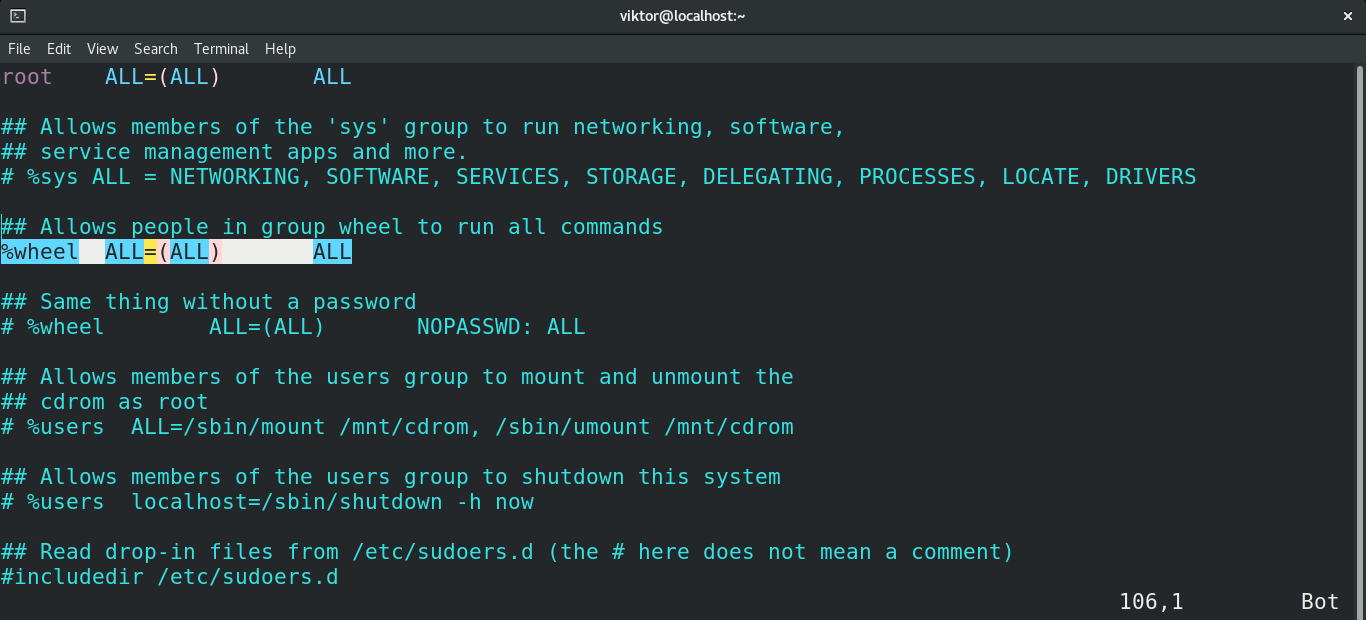
To draw attention to a sudo prompt in a background terminal, users can simply make it echo a bell character:ĭefaults passprompt=" ^G password for %p: " The prompt timeout can also be disabled and since that does not serve any reasonable security purpose it should be the solution here: Both of these have negative security implications. Common advice is to enable passwordless sudo, or extend the timeout of sudo remembering a password. This leads to a sudo password prompt which goes unnoticed and times out, at which point the process dies and the work done is lost or, at best, cached. Tips and tricks Disable password prompt timeoutĪ common annoyance is a long-running process that runs on a background terminal somewhere that runs with normal permissions and elevates only when needed. These permissions are set by default, but if you accidentally change them, they should be changed back immediately or sudo will fail. The file permissions must be set to 0440. The owner and group for the sudoers file must both be 0. Otherwise, see the sudoers(5) for detailed information. USER_NAME HOST_NAME= NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/halt,/usr/bin/poweroff,/usr/bin/reboot,/usr/bin/pacman -SyuĪ detailed sudoers example is available at /usr/share/doc/sudo/examples/sudoers. In particular such a line should be after the %wheel line if your user is in this group.Įnable explicitly defined commands only for user USER_NAME on host HOST_NAME without password: Note: The most customized option should go at the end of the file, as the later lines overrides the previous ones. To allow members of group wheel sudo access: To allow a user to run all commands as any user but only on the machine with hostname HOST_NAME:
CREATE A USER WITH SUDO PRIVILEGES LINUX FULL
To allow a user to gain full root privileges when they precede a command with sudo, add the following line: # Set default EDITOR to restricted version of nano, and do not allow visudo to use EDITOR/VISUAL.ĭefaults editor=/usr/bin/rnano, !env_editor To change the editor of choice permanently system-wide only for visudo, add the following to /etc/sudoers (assuming nano is your preferred editor): To change the editor permanently, see Environment variables#Per user.
This might come in handy in case you want to circumvent locking the file with visudo. To establish nano as the visudo editor for the duration of the current shell session, export EDITOR=nano to use a different editor just once simply set the variable before calling visudo:Īlternatively you may edit a copy of the /etc/sudoers file and check it using visudo -c /copy/of/sudoers. The sudo package is compiled with -with-env-editor and honors the use of the SUDO_EDITOR, VISUAL and EDITOR variables. visudo(8) warns that configuring visudo to honor the user environment variables for their editor of choice may be a security hole, since it allows the user with visudo privileges to run arbitrary commands as root without logging simply by setting that variable to something else.Always edit it with visudo to prevent errors.
CREATE A USER WITH SUDO PRIVILEGES LINUX FREE


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
